

However, the fact that amputation as a curative treatment strategy for sarcomas in the extremities has no survival benefit when compared to limb-preserving surgical procedures should be taken into account. In cases with extensive infiltration of functional structures, amputation still has to be considered as a treatment option in order to obtain clear margins ( 7, 11, 12). Dedifferentiated and high tumor grade is also associated with higher invasiveness, resulting in extensive infiltration of the surrounding tissues. Most survival studies have revealed that the tumor grade is the most significant prognostic factor ( 9, 10). However, large tumor size is found more frequently in high-grade tumors.

Regarding tumor size, large soft-tissue sarcomas are shown to have a diminished survival when compared with small tumors. Deep or subfascial localization is associated with a higher risk of local recurrence or distant metastasis when compared with superficial or epifascial localization ( 7– 9). Regarding surgical resectability, the localization of the tumor is of great relevance. The factors that determine the resectability of sarcomas are mainly the tumor size and localization. Oncological Treatment Strategies and ConceptsĬontemporary treatment strategies should include concepts of complete resection with negative surgical margins in combination with plastic reconstructive surgery, especially considering the postoperative functional aspects. Whether limb preservation or ablative procedures are applied is also determined by the location of the tumor and the expectations and the functional demands of the patient. In these circumstances, plastic surgical techniques can frequently reduce functional impairment and cover soft-tissue defects, particularly in cases of large tumor size or localization adjacent to critical anatomic structures, thereby improving the quality of life for these patients. However, in patients with locally advanced soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities, attainment of negative surgical margins may require extensive surgery and could result in a loss of extremity function. The data within the latter suggested that patients with clear margins had a better prognosis, but surgery to preserve functionality may result in very close margins without impairing survival. Interestingly, a recently published meta-analysis revealed that the width of negative surgical margins has no significant impact on overall survival ( 6). Primary amputations have been increasingly replaced by limb-sparing techniques, preserving extremity function as much as possible ( 3, 5). The local treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas has undergone major changes over the last few decades. Other rare malignancies with localization at the foot are, for example, tumors of the skin, such as melanoma, and giant cell tumors of the tendon-sheath, vascular sarcomas, and carcinoma metastases. Regarding the content of soft tissues, the lower extremities are affected more frequently than the upper extremities, with a ratio of 3:1.
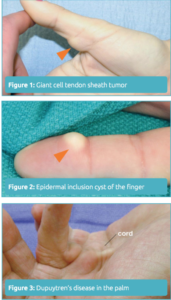
Soft-tissue sarcomas, as rare tumors of mesenchymal origin, account for about 1% of all adult malignancies but are located in the extremities in about 60% of all cases ( 4). Malignant neoplasms on the foot and ankle make up about 4% of all bone and soft-tissue tumors of the body ( 1– 3).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
